Overview on current vaccine studies against COVID-19 worldwide
When the Europeans invaded the South American territories in the 16th century, they also brought infectious diseases from Europe into the newly conquered territories, with some disastrous consequences for the indigenous population living there [1]. The reason for this was a lack of immunity of the South American population against the foreign pathogens from Europe. Such a scenario impressively illustrates how important an existing immunity, acquired through natural exposure to the pathogen or , in modern times, through a vaccination, is for the vulnerability against a pathogen. In order to reduce the danger posed to humans by the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, a suitable vaccine is therefore feverishly sought worldwide.
Numerous research teams are currently working on this task. A large number of possible vaccine platforms are currently being investigated (overview by Le et al in Nature Reviews, [2], Fig. 1).
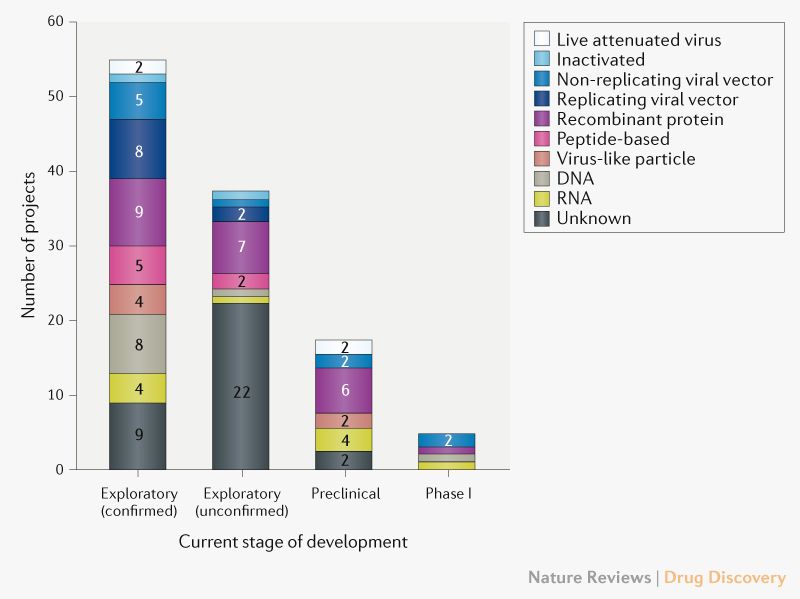
Fig. 1: Pipeline with vaccine candidates against COVID-19 grouped by technology platform. Exploratory projects (subgrouped in confirmed and unconfirmed) are in an early planning stage without in-vivo-tests, and preclinical studies are in the stage of in-vivo-tests and/or the production of material for clinical studies. Source: Le et al, Nature Reviews Drug Discoveries [2]
All vaccines aim to expose the body to an antigen that does not cause disease but produces an immune response that can block or kill the virus when a person becomes infected. For an illustrative explanation of how the different types of vaccines tested against the corona virus work, see a review article by Nature.
In addition, the Vaccine Centre at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine provides a tracker on its website that allows COVID-19 vaccine candidates to be tracked as they progress through the development phases. The status is updated weekly. To the vaccine tracker
Clinical studies
The global pandemic has led to a strong emphasis on research into a suitable vaccine against COVID-19. In the meantime, some vaccine candidates have already made it into clinical trials. Below you will find an overview of the vaccine candidates that have already been approved for clinical trials.
Tab. 1: Overview of the vaccine candidates approved for clinical trials (updated: 15.07.2020)
vaccine candidate |
developer/ sponsor |
technology |
phase |
location |
registration no/ link |
period |
applied also for... |
|
Ad5-nCoV |
CanSino Biologics, Institute of Biotechnology of the Academy of Military Medical Sciences |
recombinant adenovirus type 5 vector |
Phase I-II |
China |
Phase 2: ChiCTR2000031781; Phase1: ChiCTR2000030906 |
March 2020 to December 2020 |
Ebola |
|
ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 |
University of Oxford |
adenovirus vector |
Phase I-III |
United Kingdom |
Phase 3: ISRCTN89951424; Phase2b/3: 2020-001228-32; Phase 1/2: PACTR202006922165132 2020-001072-15 |
April 2020 to May 2021 |
MERS, influenza, TB, Chikungunya, Zika, MenB, plague |
|
BNT162 (a1, b1, b2, c2) |
BioNTech; Fosun Pharma; Pfizer |
RNA |
Phase I-II |
Germany |
April 2020 to May 2021 |
||
|
unnamed |
Sinovac Biotech |
inactivated SARS-CoV-2 virus |
Phase I-III |
China |
Phase 3: NCT04456595 |
April 2020 to December 2020 |
SARS |
|
INO-4800 |
Inovio Pharmaceuticals, CEPI, Korea National Institute of Health, International Vaccine Institute |
DNA plasmid delivered by electroporation |
Phase I-II |
United States, South Korea |
April 2020 to November 2020 |
Lassa, Nipah, HIV, Filoviris, HPV, Cancer indications, Zika, Hepatitis B |
|
|
mRNA-1273 |
Moderna, US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases |
lipid nanoparticle dispersion containing messenger RNA |
Phase I-III |
United States |
Phase 3 (not yet recruiting):NCT04470427 Phase 2: NCT04405076 |
March 2020 to 2021 |
multiple candidates |
|
Covid-19/aAPC |
Shenzhen Geno-Immune Medical Institute |
lentiviral vector, pathogen-specific artificial antigen presenting dendritic cells |
Phase I |
China |
March 2020 to 2023 |
||
|
LV-SMENP-DC |
Shenzhen Geno-Immune Medical Institute |
lentiviral minigene vaccine, dendritic cells modified with lentiviral vector |
Phase I |
China |
March 2020 to 2023 |
||
|
bacTRL-Spike |
Symvivo Corporation, University of British Columbia, Dalhousie University |
DNA, bacterial medium (oral |
Phase I |
Canada |
April 2020 to December 2021 |
||
|
CHO Cell |
Anhui Zhifei Longcom Biopharmaceutical/ Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
Protein Subunit: Adjuvanted recombinant protein (RBDDimer) |
Phase I-II |
China |
Phase 2: NCT04466085; Phase 1: NCT04445194 |
July 2020 to December 2021 |
MERS |
|
AG0301-COVID19 |
Osaka University/ AnGes/ Takara Bio |
DNA plasmid vaccine + Adjuvant |
Phase I-II |
Japan |
Phase 1/2: NCT04463472 |
June 2020 to July 2021 |
|
|
unnamed |
Cadila Healthcare Limited |
DNA plasmid vaccine |
Phase I-II |
India |
Phase 1/2: CTRI/2020/07/026352 (not yet recruiting) |
||
|
unnamed |
Beijing and Wuhan Institute of Biological Products/Sinopharm |
Inactivated |
Phase I-II |
China |
Phase 1/2: ChiCTR2000031809; ChiCTR2000032459 |
||
|
BBV152 |
Bharat Biotech |
Whole-Virion Inactivated |
Phase I-II |
India |
Phase 1/2: CTRI/2020/07/026300 |
July 2020 |
|
|
SARS-CoV-2 rS |
Novavax |
Full length recombinant SARS CoV-2 glycoprotein nanoparticle vaccine |
Phase I-II |
Australia |
Phase 1/2: NCT04368988 |
May 2020 to July 2021 |
RSV; CCHF, HPV, VZV, EBOV |
|
GX-19 |
Genexine Consortium |
DNA Vaccine |
Phase I |
Korea |
June 2020 to June 2022 |
||
|
unnamed |
Institute of Medical Biology , Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences |
Inactivated |
Phase I |
China |
May 2020 to September 2021 |
||
|
Gam-COVID-Vac |
Gamaleya Research Institute |
NonReplicating Viral Vector Adeno-based |
Phase I |
Russia |
June 2020 to August 2020 |
||
|
SCB-2019 |
Clover Biopharmaceuticals Inc./GSK/Dynavax |
Native like Trimeric subunit Spike Protein vaccine |
Phase I |
Australia |
June 2020 to March 2021 |
HIV, REV Influenza |
|
|
COVAX19 |
Vaxine Pty Ltd/Medytox |
Recombinant spike protein with Advax™ adjuvant |
Phase I |
Australia |
June 2020 to July 2021 |
||
|
SARS-CoV-2 Sclamp vaccine |
University of Queensland/CSL/Seqirus |
Molecular clamp stabilized Spike protein with MF59 adjuvant |
Phase I |
Australia |
Nipah, influenza, Ebola, Lassa |
||
|
COVAC1 |
Imperial College London |
LNP-nCoVsaRNA |
Phase I |
England |
June 2020 to July 2022 |
EBOV; LASV, MARV, Inf (H7N9), RABV |
|
|
CVnCoV Vaccine |
Curevac AG |
mRNA |
Phase I |
Germany |
June 2020 to August 2021 |
RABV, LASV, YFV; MERS, InfA, ZIKV, DENV, NIPV |
|
|
unnamed |
People's Liberation Army (PLA) Academy of Military Sciences/Walvax Biotech |
mRNA |
Phase I |
China |
|||
|
Coronavirus-Like Particle COVID-19 Vaccine |
Medicago Inc. |
Plant-derived VLP adjuvanted with GSK or Dynavax adjs. |
Phase I |
Canada |
July 2020 to April 2021 |
Flu, Rotavirus, Norovirus, West Nile virus, Cancer |
In addition, numerous vaccine candidates are being investigated worldwide in laboratory and animal studies. At present, it appears that ferrets as well as guinea pigs and genetically modified mice could be suitable as model systems for research into SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates. The WHO maintains a list of candidates currently in the preclinical investigation phase. You can find the WHO list online here. The Milken Institute has also compiled a comprehensive overview of ongoing studies on drugs and vaccines for COVID-19. You can find the overview online here.
An interview about vaccine development with a member of the internal advisory board of the Zoonoses Platform, PD Dr. Michael Mühlebach, you can find here.
Literature:
1. Vagene, A.J., et al., Salmonella enterica genomes from victims of a major sixteenth-century epidemic in Mexico. Nat Ecol Evol, 2018. 2(3): p. 520-528.
2. Thanh Le, T., et al., The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2020.